In
this article, I review the scientific literature showing that toxic
heavy metals and microplastics have a synergistic toxic effect. This has
been well established in environmental studies. EDTA is used for
detoxification of contaminated soils and wastewater, which should be of
interest in people who have heavily contaminated soils and want to grow
their own food. Plants uptake the toxic metals that are sprayed via
military geoengineering operations, poisoning our biosphere - thus
affecting even the most environmentally aware soils and water. Heavy
metals testing of soil and water is commercially available.
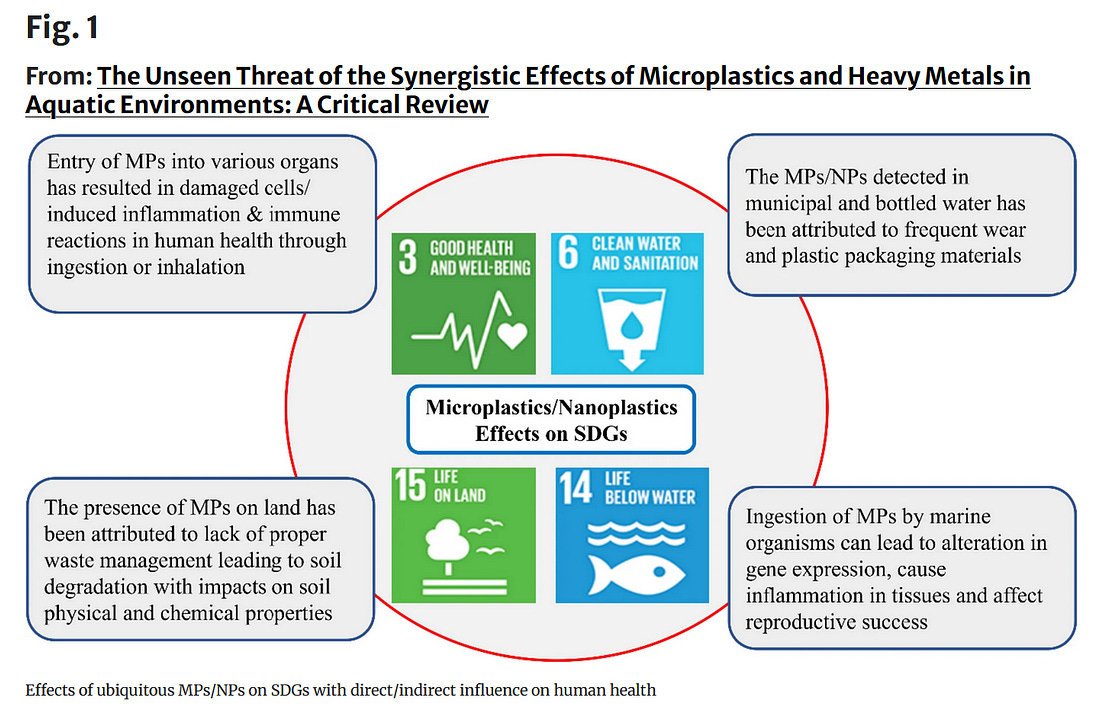
The Unseen Threat of the Synergistic Effects of Microplastics and Heavy Metals in Aquatic Environments: A Critical Review
The
interplay between MPs and other chemical contaminants, including heavy
metal ions and organic contaminants, has raised significant health
concerns for both humans and aquatic life [13, 15, 20].
The rough surfaces and numerous functional groups of MPs enable the
attachment of heavy metals and organic contaminants, influencing their
environmental behaviour [8, 17].
Heavy metals are hazardous contaminants and can persist with
threatening impacts on ecosystems, food quality, and human health safety
Recent
studies have revealed the adsorption capacity of both new and aged MPs
with heavy metals like Pb, Cr, Fe, Zn, Sn, Ti, Mn, Al, Cu, and Ni, in
aqueous environments However, there exists a remarkable scarcity of
research concerning the adsorption of metals. In particular, minimal
effort has been made to comprehend the mechanisms governing the sorption
interactions between MPs and heavy metals.
The synergistic toxicity of metals and microplastics in fish is also reported:
A
recent research revealed that when zebrafish were exposed to both MPs
(specifically polystyrene) and Cd, they experienced oxidative harm and
inflammation. Moreover, there was a heightened accumulation of Cd in
their liver, intestines, and gills. This combined exposure amplified the
detrimental effects of Cd on the fish’s tissues
In
humans, microplastics increase the stroke risk by 51 times, make people
4.5 times more likely to have a heart attack and it is well known that
heavy metals like lead increase cardiovascular mortality by >50%.
Plaque buildup in the necks of stroke survivors may be loaded with microplastics
The
concentration of so-called micronanoplastics in carotid arteries was 51
times higher in plaque from people who'd had a stroke, mini-stroke or
temporary blindness compared to amounts found in the walls of
plaque-free carotid arteries. Even people with carotid artery plaque who
had not experienced any of those conditions still had 16 times more
micronanoplastics in their plaque.
Toxic metals like Lead are known to increase cardiovascular and all cause mortality.
The
association between whole-blood lead concentration and all-cause or
cardiovascular disease mortality in hypertensive patients
Lead has a half life of 30 years in the body and bioaccumulates in the bone.
Do We Underestimate Risk of Cardiovascular Mortality due to Lead Exposure?
The
findings suggest that the true cardiovascular mortality effects of lead
exposure in the US could be approximately 1.5 to 2 times greater than
what has been previously.
The
estimated number of CVD deaths attributable to lead exposure in the US
was approximately 180,000 annually if blood lead was used as an exposure
marker, but this number would double to 360,000 deaths per year if
predicted tibia lead was used instead. These results suggest that risk
assessments based on BLLs may underestimate the actual mortality risk of
lead exposure. We also confirm that predicted bone lead variables were
associated with CVD mortality independent of the predictors of bone lead
markers
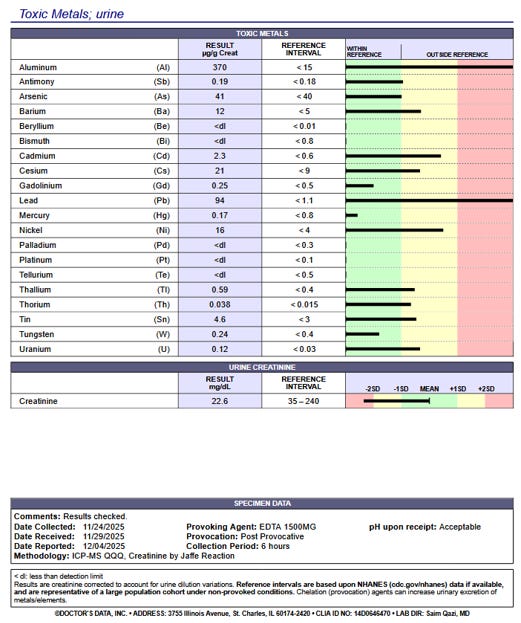
EDTA
increases excretion of Lead by 4800%. Of note, most humans have
synergistic high levels of multiple toxic metals as shown in the heavy
metals test below.
I
have previously discussed microplastics and have pointed out that the
Moderna patent admits that Stealth plastic nanoparticles are within the
COVID19 injections. Understanding now the findings of significant
increases of microplastics in human tissue, plus the fact that we are
being poisoned by heavy metals in vaccines, food, drinking water - makes
the consideration of detoxification more reasonable. The toxicity of
microplastics and metals are synergistic-ally enhanced as discussed
above.
We know that 55 toxic metals were found within the COVID19 injections.
Argentinian
Heroic Scientists Are Persecuted For Their Research Of COVID19
Bioweapons & Finding 55 Undeclared Toxic Elements. Sign Petition NOW
In Support Of Drs. Marcela Sangorin & Lorena Diblasi
Health
Impact of Microplastics: A Review of Environmental Distribution, Human
Exposure, Toxic Effects And Relationship To Chronic Diseases
Microplastics in Human Blood: Polymer Types, Concentrations and Characterization Using μFTIR
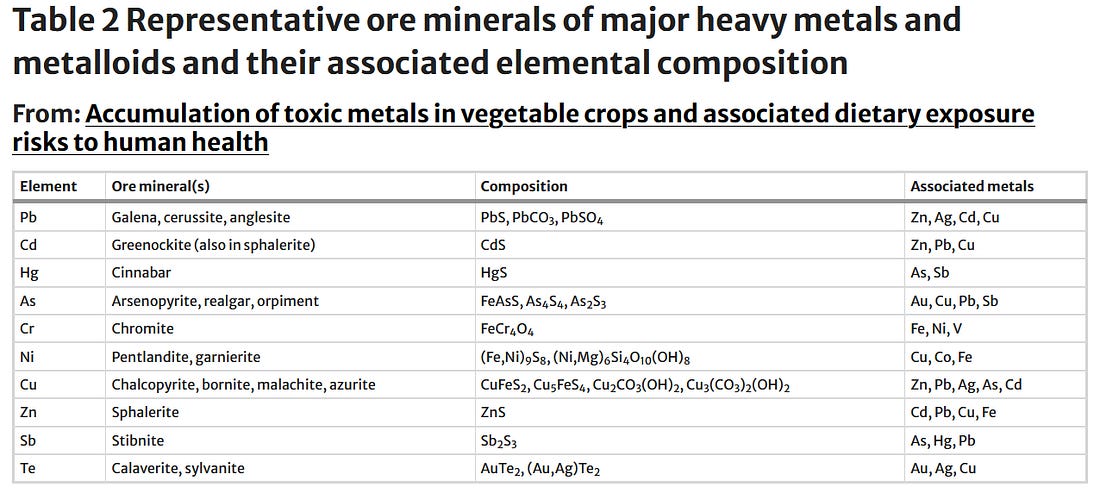
Accumulation of toxic metals in vegetable crops and associated dietary exposure risks to human health
Heavy
metal contamination in food systems has emerged as a critical global
concern due to its persistent nature and serious implications for food
safety and public health. Rapid industrialization, urban expansion, and
unsustainable agricultural practices especially the use of untreated
wastewater for irrigation have contributed significantly to the
accumulation of toxic metals in agricultural soils and edible crops.
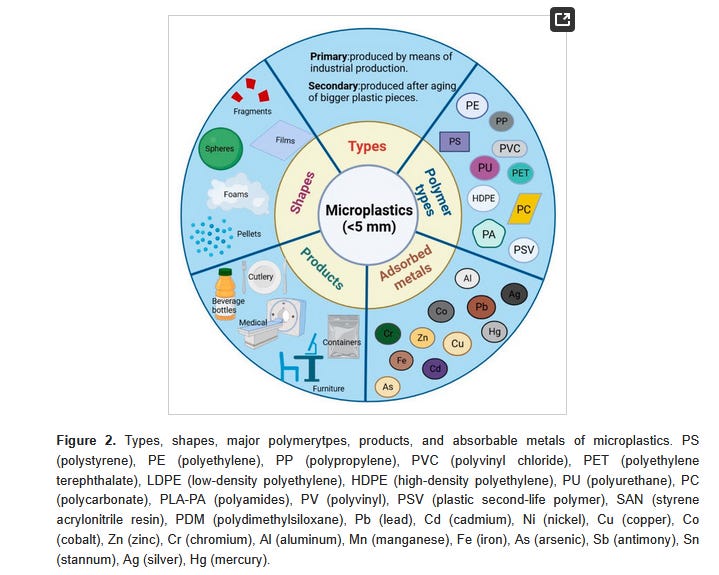
Different microplastics have variable absorption rates of heavy metals.
Factors Affecting the Adsorption of Heavy Metals by Microplastics and Their Toxic Effects on Fish
Fish
not only constitute an important trophic level in aquatic ecosystems
but also serve as an important source of protein for human beings. The
health of fish is related to the sustained and healthy development of
their entire aquatic ecosystem. Due to the widespread use, mass
production, high disposal frequency, and degradation resistance of
plastics, these pollutants are released into aquatic environments on a
large scale. They have become one of the fastest growing pollutants and
have a substantial toxic effect on fish. Microplastics have intrinsic toxicity and can absorb heavy metals discharged into water. The
adsorption of heavy metals onto microplastics in aquatic environments
is affected by many factors and serves as a convenient way for heavy
metals to migrate from the environment to organisms. Fish are exposed to
both microplastics and heavy metals. In this paper, the toxic effects
of heavy metal adsorption by microplastics on fish are reviewed, and the
focus is on the toxic effects at the individual (survival, feeding
activity and swimming, energy reserves and respiration, intestinal
microorganisms, development and growth, and reproduction), cellular
(cytotoxicity, oxidative damage, inflammatory response, neurotoxicity,
and metabolism) and molecular (gene expression) levels. This facilitates
an assessment of the pollutants’ impact on ecotoxicity and contributes
to the regulation of these pollutants in the environment.
EDTA has been used to decontaminate soil, water, animals and humans:
Use
of EDTA and CaCl[sub.2] Extraction Methods to Predict the
Bioavailability of Heavy Metals in Soils Polluted with Microplastics.
There
is growing concern about microplastics entering the food chain, as the
surface of chemically active microplastics (MPs) allows them to absorb
toxic contaminants, e.g., heavy metals [1], modifying their mobility and
bioavailability in soil and, thus, causing a risk of higher
accumulation of metals in plants and micro-organisms.
Using
single extraction methods for predicting the bioavailability of heavy
metals (HMs) in polluted soils has always been challenging. There is no
consensus about a methodology in which extractants indicate the
bioavailability of HMs close to natural soil conditions with the impact
of root exudates. The uptake of metals by plants is mostly facilitated
by the exchangeable and water-soluble fractions of metal, which can be
indicated by the use of single extraction protocols using weak acids,
salts, or chelating agents like EDTA. EDTA is a powerful chelating agent
that can extract a wide range of heavy metals from soil. It is highly
effective in mobilizing metals by forming stable metal complexes, which
can include metals bound to organic matter and other soil fractions.
Studies have shown that EDTA can extract high concentrations of metals,
such as Pb, Cd, Cu, and Zn, from contaminated soils and sediments [26].
For example, EDTA extracted the highest concentrations of soil-borne
metals compared to other extractants like tartaric acid and water [27].
The efficiency of removing HMs from soil depends on many factors, such
as the speciation of HMs in soil, the strength of EDTA, the presence of
other cations in the solution, and soil pH. EDTA is a strong chelating
agent that is widely used for extracting heavy metals from soil,
This
study provides critical insights into the intricate interactions
between microplastics (MPs), heavy metals (HMs), and soil properties,
demonstrating their significant impact on metal bioavailability,
sorption processes, and soil chemistry. The findings indicate that the
presence of MPs alters soil pH, with polyester (PES) and high-density
polyethylene (HDPE) leading to the most pronounced pH increases. These
pH changes influence metal mobilization and immobilization, affecting
extraction efficiency and the overall risk associated with heavy metal
contamination. The comparison of extraction methods revealed that 0.05 M
EDTA was more effective in mobilizing metals from soil, whereas 0.01 M
CaCl[sub.2] provided a more ecologically relevant measure of
bioavailable metal fractions. This highlights the importance of
selecting appropriate extraction techniques when assessing metal
contamination risks. Additionally, the sorption experiments demonstrated
that MPs serve as additional adsorption sites, with HDPE enhancing Pb
immobilization while increasing the mobility of Cd and Co. These results
confirm the dual role of MPs in regulating metal behavior, either
facilitating immobilization or promoting mobility, depending on specific
metal–polymer interactions. The implications of these findings extend
beyond laboratory conditions, emphasizing the need for more
sophisticated approaches to predict and mitigate the combined impact of
MPs and HMs on soil health.
The cleaning of wastewater with EDTA from poisonous toxic metals has been performed since 1948:
Effects of EDTA on Wastewater Treatment
It turns out that EDTA even eliminated antibiotics and other pharmaceutical drugs from wetlands:
Enhanced
Removal of Common Wastewater-Derived Trace Organic Contaminants in
Vertical-Flow Constructed Wetlands Amended with Fe(III)-EDTA
The
study combined a 7-month monitoring campaign, 3 different hydraulic
regimes, and soil extraction data to elucidate the effects of the
amendment on the fate of the TrOCs within the systems. Our results
indicate that Fe-EDTA contributed to the degradation of carbamazepine
and sulfamethoxazole under the studied flow regimes. Iron-amended soil
columns (n = 5/9 columns fed for 7 months with
synthetic domestic wastewater) removed 12 ± 19% of influent
carbamazepine (the most recalcitrant TrOC included in the study), 18%
higher than the control columns. Operating the columns with periods of
retention and discharge further improved carbamazepine and
sulfamethoxazole removal efficiency (removal increased to 49 ± 7.6% and
81 ± 9.2% of influent concentrations, respectively). The more readily
degradable compounds atenolol and trimethoprim were removed with >97%
efficiency in both control and amended columns, regardless of flow.
It is capable of removing toxic heavy metals AND organic pollutants such as pesticides, herbicides, and oil spill contaminants.
The Application of EDTA in Wastewater Treatment
EDTA
(Ethylenediamine Tetraacetic Acid) is a versatile chemical that has
found extensive applications in various industries, including wastewater
treatment. This article will explore the role of EDTA in wastewater
treatment and its benefits for water quality improvement.
Understanding EDTA’s Properties
Industrial grade EDTA
is a highly effective chelating agent that can bind to metal ions such
as calcium, iron, copper, zinc, and magnesium. Its primary function is
to prevent these metal ions from interacting with each other and forming
insoluble complexes, which can cause hardness, staining, and corrosion
in water. By chelating these metal ions, EDTA helps to maintain the
balance of essential minerals in water and promote better water quality.
Application of water cleaning agent EDTA in Wastewater Treatment
EDTA
is widely used in wastewater treatment processes to remove heavy metals
and organic pollutants. Some of the key applications of EDTA in
wastewater treatment are:
1.
Heavy Metal Removal: EDTA is effective in removing a wide range of
heavy metals from wastewater, including lead, mercury, cadmium, zinc,
and copper. The chelation of these metal ions by EDTA prevents them from
causing environmental pollution and potential health hazards.
2.
Organic Pollutant Degradation: EDTA can also adsorb organic pollutants
such as pesticides, herbicides, and oil spill contaminants. The removal
of these organic pollutants not only improves water quality but also
protects aquatic life and ecosystems.
EDTA has been used for detoxification of many animal species, here is more information:
Heavy Metal Poisoning in Dogs and EDTA
__________________________________________________________________
CLINICAL APPLICATION IN HUMANS
I
have been discussing the versatility and usefulness of EDTA Chelation
to remove toxic heavy metals, as an antidote for the COVID19 bioweapon, a
significant reversal of autoimmune diseases from toxic metal exposure.
You can find prior substack articles on the subject here:
Literature Review of EDTA Chelation
EDTA Detoxification for Metals, Graphene and Hydrogel
EDTA Chelation Dissolves the Artificial Intelligence Magnetic Hydrogel Weapon
THERE IS HOPE - EDTA CHELATION WORKS and What Really IS COVID???
Decontaminating The Blood From Synthetic Biology Hydrogel With EDTA Chelation - Live Blood Documentation
Breaking
News: Calcium Disodium EDTA +Vitamin C Deactivates Nano/Microrobots And
Dissolves All Microchips In Pfizer COVID19 “Vaccine”- Darkfield
Microscopy
As
part of a comprehensive cancer treatment, a stage four prostate cancer
patient with severe fatigue and cognitive decline, weight loss, gait
abnormality was treated by me palliative with EDTA Chelation, in
addition to intravenous high dose Vitamin C, Artesemia annua, DMSO, and
multiple other interventions. His provoked heavy metals test showed
significant toxicity with both Aluminum and Lead, in synergistic
addition with other heavy metals like Uranium, Mercury, Cadmium and
others. All can contribute to development of cancer as well as
significant cognitive impairment which is reversible. Within 2 weeks of
comprehensive treatment the patient achieved a significant improvement
in overall wellbeing, with improvement of cognition, energy, gait and
quality of life.
Given
synergistic toxicity of metals and microplastics detoxification with
EDTA Chelation could be considered in such cases, given the extreme
environmental pollution problem caused not just by industrial
contamination but poisoning from military weather warfare geoengineering
operations.
Farmers
could consider to detoxify the soil from the geoengineering
contamination with the above mentioned EDTA methods after soil sampling.
Consulting experts should be considered.
Heavy metals testing at AM Medical after IV use of 1500mg EDTA Chelation showing significant synergistic heavy metal toxicity.
Please
note I use EDTA, Vitamin C and DMSO and other molecules depending on
severity of symptoms. I started using Intravenous and oral DMSO last
year in my clinical practice, and it has been magnificent in its many
benefits and you can read great articles about its beneficial effects
written by the The Midwestern Doctor. DMSO can extract plastics and
metals and I have noticed significant improvement in detoxification as
well as treatment when adding DMSO to the IV and oral treatments.
Researcher Maria Crisler showed benefits of DMSO on micro-technology
contamination of blood a couple years ago. Plastics and metals
extraction with DMSO has been studied as well:
Toxicity assessment of DMSO extracts of environmental aged beached plastics using human cell lines
I talk about many other treatment interventions in my books Light Medicine and Transhuman.


No comments:
Post a Comment