Jared Taylor • July 26, 2021
How many times have you heard that slavery was “America’s original sin”? I’m not quite sure what that means, but I think the idea is that slavery was a uniquely horrible thing that defines the United States and will stain whites forever. It’s one of the few things Senate Minority Leader Mitch McConnell and Barack Obama agree on. There are books about it. Here’s a college course at UC Davis called “Slavery: America’s Original Sin: Part 1.”
The fact is, there has been slavery in every period of history, and just about everywhere. The Greeks and Romans had it, the ancient Egyptians had it, it’s all over the Bible, the Chinese and the pre-Columbian Indians had it, the Maoris in New Zealand had it, and the Muslims had it in spades. But I have never, ever heard of slavery being anyone else’s “original sin.”
About the only societies that never had slaves were primitive hunter-gatherers. As soon as people have some kind of formal social organization, they start taking slaves.
You’ve heard about slavery and mass human sacrifices of Central and South American Indians, but North American Indians were enslaving each other long before the white man showed up.
Tlingit and Haida Indians, who lived in the Pacific Northwest, went raiding for slaves as far South as California. About one quarter of the population were slaves, and the children of slaves were slaves. During potlatches, or huge ceremonial feasts, the Tlingit would sometimes burn property and kill slaves, just to show how rich they were. What’s a couple of slaves to a guy who lives in a house like this?
When we bought Alaska from the Russians in 1867, Indians were furious when we told them they had to give up their slaves. The Tlingit carved this image of Abraham Lincoln, the emancipator, to try to shame the government into compensating them for slaves.
What were called the Five Civilized Tribes of the American Southeast happily bought black slaves. In 1860, there were 21,000 Cherokee, and they owned 4,000 slaves. And that was just the Cherokee. Many took their slaves with them when they were forced to move Wes t.
Free blacks in the South owned slaves. The fact of having been slaves didn’t stop them from wanting to be slave masters themselves. In 1840, in South Carolina alone, there were 454 free blacks who owned a total of 2,357 slaves. Only about 20 percent of Southern households had even one slave, but 75 percent of the free-black households in South Carolina owned slaves.
Don’t believe me? It’s all in this book by the expert on the subject, Larry Koger of the University of South Carolina. And he demolishes the idea that most blacks bought slaves only to get family members out of slavery. Like whites, some were kind masters and some were mean, but, for the most part, they owned slaves for exactly the same reasons whites did.
There’s a whole book about this black guy, Andrew Durnford.
He had a plantation of 672 acres along the Mississippi in Louisiana, and close to 100 slaves. Another black slave owner in Louisiana, P.C. Richards, owned 152 slaves. Black slaveowners avidly supported the Confederacy. There are no accurate estimates of the number of slaves held by free blacks at the time of the Civil War, but they would have been tens of thousands.
If slavery is somebody’s Original Sin, it’s sure not ours. Take a look at this map of the slave trade, beginning in 1500.
[Source: SlaveVoyages.com, click to enlarge]
The thicknesses of the lines represent numbers of slaves. What became the United States imported just 400,000 slaves—about 3 percent of all the slaves who crossed the Atlantic. Look at all the slaves who went to Brazil and to the Caribbean Islands. They needed millions because, unlike American slaveowners who raised slave families, they bought grown men and worked them to death. And let us not forget, virtually every slave on this map was caught by blacks or Arabs.
And look at all the slaves who ended up in North Africa and the Middle East.
That’s millions of them going to Muslim countries at exactly the same time slaves were crossing the Atlantic. And Arabs had been taking black slaves out of Africa, across the Sahara, for 900 years before America was even discovered—and a forced march across the desert was a lot worse than crossing the Atlantic. In this article about Africa’s first slavers—the Arabs—historian Paul Lovejoy estimates that over the centuries, Muslims took about 14 million blacks out of Africa [Recalling Africa’s harrowing tale of its first slavers – The Arabs – as UK Slave Trade Abolition is commemorated, March 27, 2018]. That is more than the 12 million who went to the New World.
And you might ask, where are the descendants of all those Middle Eastern slaves? America has millions of slave descendants. Why don’t you see lots of blacks in Saudi Arabia or Syria or Iraq? Arabs castrated black slaves so they wouldn’t have descendants.
Muslims were even more enthusiastic about enslaving white people. Christian Slaves, Muslim Masters, by Prof. Robert C. Davis is the best book on the subject. Remember the Barbary Pirates of North Africa? Between 1530 and 1780 they caught and enslaved more than a million white, European Christians. During the 16th and 17th centuries, Arabs took more white slaves south across the Mediterranean than there were blacks shipped across the Atlantic.
Mostly, Muslim pirates captured European ships and stole their crews. In just three years, from 1606 to 1609, the British navy admitted it had lost 466 British merchant ships to North African pirates [Counting European Slaves on the Barbary Coast Past & Present, August 2001]. Four hundred sixty-six ships in just three years. Arabs took American slaves. Between 1785 and 1793 Algerians captured 13 American ships in the Mediterranean and enslaved the crews. This is a 1804 battle between Arab pirates and the USS Enterprise.
It was only in 1815, after two wars, that the United States was finally free of the Barbary pirates.
Muslim pirates also organized huge, amphibious slave-catching assaults that practically depopulated the Italian coast. In 1544, Algerian raiders took 7,000 slaves in the Bay of Naples in a single raid. This drove the price of slaves so low it was said you could “swap a Christian for an onion.”
After a 1566 raid on Granada in Spain netted 4,000 men women, and children, it was said to be “raining Christians in Algiers.” Women were easier to catch than men, and were prized as sex slaves, so some coastal areas lost their entire child-bearing populations. One raid as far away as Iceland brought back 400 white slaves.
Prof. Davis notes that the trade in black Africans was strictly business, but Muslims had a jihad-like enthusiasm for stealing Christians. It was revenge for the Crusades and for the reconquest of Spain from the Arabs in 1492. When Muslim corsairs raided Europe, they made a point of desecrating churches and stealing church bells. The metal was valuable but stealing church bells silenced the voice of Christianity.
It was a tradition to parade newly captured Europeans through the streets so people could jeer at them, while children threw garbage at them. At the slave market, both men and women were stripped naked to evaluate their sexual value. In the North African capitals—Tunis, Algiers, Tripoli—there was a big demand for homosexual sex-slaves. Other Europeans were worked to death on farms or building projects.
Prof. Davis writes that unlike in North America, there were no limits on cruelty: “There was no countervailing force to protect the slave from his master’s violence: no local anti-cruelty laws, no benign public opinion, and rarely any effective pressure from foreign states.” Slaves were not just property, they were infidels, and deserved whatever suffering a master meted out.
For a man, there was a fate even worse than being a sex slave. Hundreds of thousands became galley slaves, often on slave-catching pirate ships. They were chained to their oars 24 hours a day, and could move only to the hole where the oar went through the hull—so they could relieve themselves. If the men were rowing, they fouled themselves. Galley slaves lived in a horrible stench, ate rotten food, were whipped by slave drivers and tormented by rats and lice. They could not lie down and had to sleep at their oars. Many never left their ships, even in port. Their job was to row until they died, and to be tossed overboard at the first sign of weakness.
Muslims have taken slaves for as long as there have been Muslims, which is about 1,400 years.
Mohammed himself was an enthusiastic slave trader. Muslims still take black slaves. As this article points out, Libya still has slave markets, Mauritanian Arabs take black slaves, and there is still slavery in Niger, Mali, Chad and Sudan[Libya’s slave markets are a reminder that the exploitation of Africans never went away, by Martin Plaut, New Statesman, February 21, 2018].
And, of course, it was white people who abolished slavery, both in their own countries and, except for a few stubborn holdouts, the whole world. Africans, just like the Tlingit Indians, screamed about all the wealth we made them give up.
But slavery’s still our “original sin.” As Time magazine wrote just this month about slavery “Europeans and their colonial “descendants” in the United States engineered the most complete and enduring dehumanization of a people in history.”[Facing America’s History of Racism Requires Facing the Origins of ‘Race’ as a Concept, by Andrew Curran, July 10, 2020]
What a small minority of Americans did for 246 years—and in a relatively mild form—is worse than anything that was ever done anywhere by anyone.
That, ladies and gentlemen, is the power of white privilege. I hope you are enjoying it.
Watch this piece on video here.
Also available on video on BitChute and Brighteon.
Jared Taylor [Email him] is the editor of American Renaissance. You can follow him on Parler and Gab.



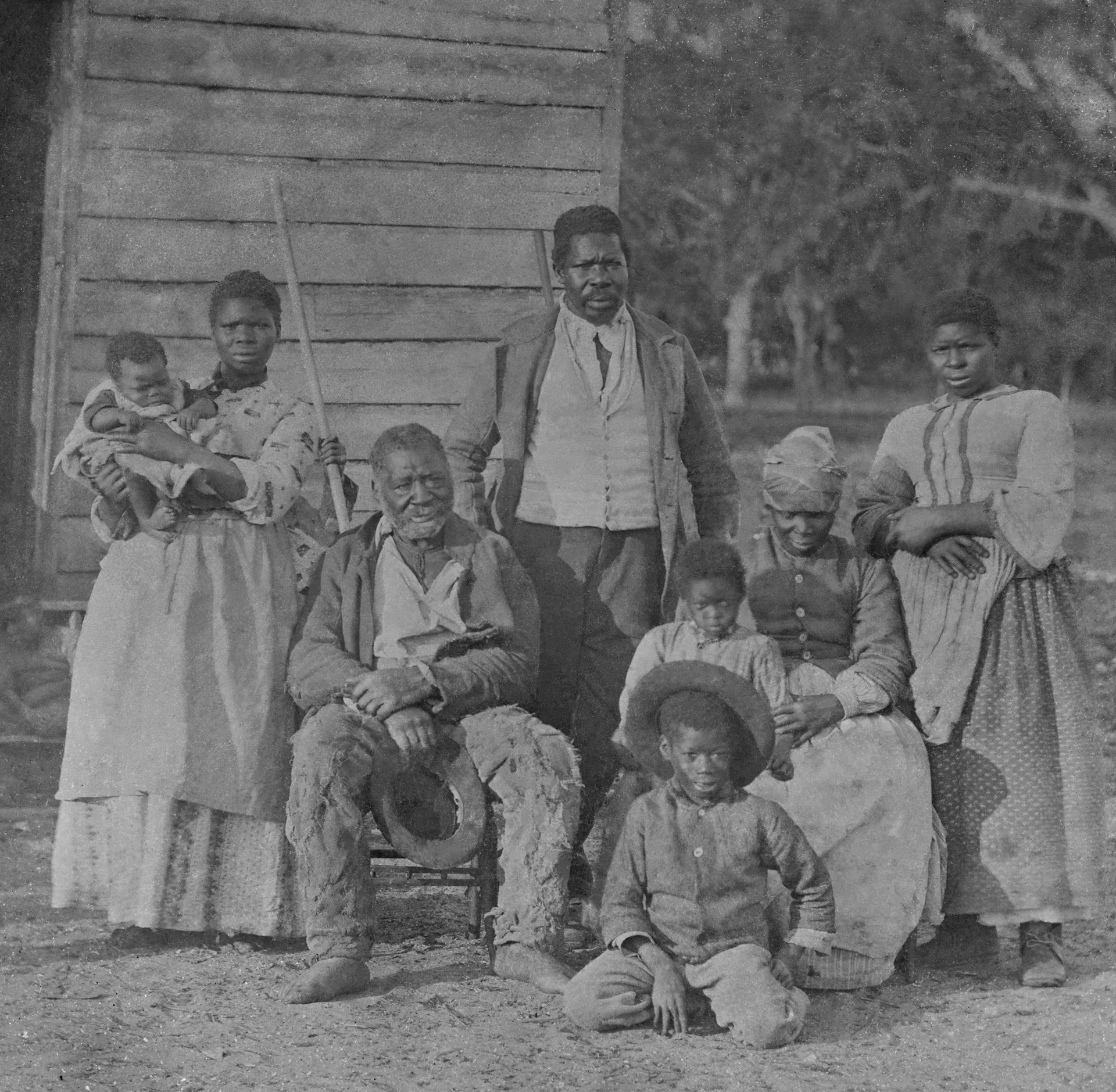







No comments:
Post a Comment