Will Your Doctor Include Nutritional Therapy In End-Of-Life Discussions?
Medicare To Incentivize Death By Paying Doctors For End-Of-Life Talks
July 13, 2015
Medicare
is now going to incentivize death by paying doctors to talk with their
patients and families about end-of-life care. Oh, they say this payment
policy would only apply to patients and their families who choose to
participate on a volunteer basis. But frankly, patients are putty in
the hands of doctors. Would the death rate rise commensurate with
Medicare payments to physicians over end-of-life issues?
The
problem for government overseers is 30% of all Medicare expenditures are
attributed to 5% of the beneficiaries who die each year with one third
of that occurring in the last month of life. [Health Services Research April 2004]
Of $554 billion spent on Medicare annually, 28 percent, or about $170 billion is spent on patients’ last six months of life. [Medicare Newsgroup June 3, 2012]
Medicare
is attempting to reduce its multi-billion bill to care for patients in
the last days of their lives. What this often represents is futile care
rather than medical care. Patients and families, in particular those
who espouse a religious faith, don’t want the doctor to “pull the plug”
because they
feel God will come through for them even against all odds.
[Journal Aging & Health Aug 2008]
Says the
doctor, according to algorithms your loved one doesn’t have a fighting
chance to survive. For example, the 5-year survival rate for pancreatic
cancer is a dismal 2%. Yet most patients fight on believing they have a
chance of beating their cancer. Doctors and hospitals are all too
willing to accommodate desperate patients and their families and bill
insurance along the way.
To
tackle this problem of futile care health care planners devised hospice
care for the dying. But wouldn’t you know it, hospice care just ended
up adding to the total medical bills, not saving money.
Now
this author has always been critical of modern medicine, especially how
hospitals and doctors run up the bill and get in all the insurance
billings they can before a patient dies.
But there
is another side to this story that reaches beyond greedy doctors and
hospitals and desperate patients and their families who are left to pray
for miracles.
How do doctors know with certainty you are going to die?
How
do doctors really know there is no hope for these so-called terminal
patients? I have heard many stories where doctors withdrew all the
medicines from a terminal patient and unplugged all the machinery and
the patient surprisingly recovered and lived a long time. Was it the
over-medication and the dungeon-like hospital rooms that were preventing
healing and recovery?
Modern
medicine is so given over to commercial interests, treating every
disease as if it were a drug deficiency and utilizing the most expensive
invasive treatments while other less costly and more effective cures
are neglected.
Save Medicare billions with sunshine vitamin D
The
predominant role sunshine vitamin D plays in health maintenance is
decades late in being recognized. Hospital rooms are devoid of
sunshine, which is the major contributor to circulating vitamin D
levels.
Vitamin
D was initially described as an essential nutrient for bone health.
Only recently has it been extolled for brain development and mood,
immunity, muscle and heart strength, and many other functions. Most
patients are admitted to hospitals in a vitamin D-deficient state,
making them prone to hospital-acquired infections and other sequelae.
A recently
published study showed that critically ill patients admitted to
intensive care units who were vitamin D deficient were 449% more likely
to die of sepsis (blood infection), kidney failure and other problems. [Critical Care March 10, 2015]
Another
study showed that more than half of patients admitted to the intensive
care unit for sepsis (blood infection) were vitamin D-deficient and were
twice as likely to die (37% versus 20%). [American Journal Critical Care Sept 2014]
Hospitalized
patients are more vulnerable to acquire infections. Over 100,000
patients die of hospital acquired infections every year (2002 figures). [Public Health Reports
March 2007] Vitamin D has antibiotic-like activity that protects
against pneumonia, blood infection (sepsis), influenza, hepatitis and
antibiotic-resistant germs that are common in hospitals. [Canadian Journal Physiology Pharmacology May 2015]
Hospitalized
patients with low vitamin D levels are far more likely to die (1 of 40)
of a deadly Clostridium difficile infection than patients with normal
vitamin D levels (1 of 93). [Journal Investigative Medicine Jan 2015]
In the
U.S. an estimated 2.61 million Clostridium difficile infections occur
annually with a mortality rate of 9% (that’s 234,900 deaths per year or
643 deaths per day!). The odds of dying from Clostridium difficile
infection in the hospital are dependent upon the season of admission
with lower rates of death during the sunnier part of the year when
vitamin D levels are high. [United European Gastroenterology April 2015]
Vitamin D and terminal cancer
Cancer is
certainly a devastating diagnosis if for not other reason than there is
no cure for cancer though there are myriads of approved treatments that
at best prolong life by a few months.
In
one study the risk of death among kidney cancer patients was reduced by
43% among patients with the highest blood concentration of vitamin D. [Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers Prevention May 28, 2015]
An
exceptional quality of vitamin D is that it may not reduce the
occurrence of cancer but certainly reduces the risk of dying from
cancer. As the blood concentration of vitamin D declines among cancer
patients their risk of dying dramatically increases. [BMC Cancer
March 8, 2015] Cancer patients housed in dungeon-like, sunless rooms
will certainly experience a decline in their vitamin D levels.
Colon-rectal
cancer has about a 2-year survival rate and there is treatment but no
cure for this form of cancer. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy do not
penetrate solid tumors such as colon-rectal cancer though both of these
treatments modalities are widely employed. Patients with the highest
blood levels of vitamin D have been shown to have a 37% reduced risk of
dying from this mortal form of cancer. [Journal Steroid Biochemistry Molecular Biology April 2015]
Vitamin D and heart disease
Vitamin D is not limited to infection and cancer. In a study involving 247,574
subjects, a total of 16 645 subjects died in 7-year period, including
5454 from cardiovascular disease. Men with the lowest versus the
highest blood concentration of vitamin D were 250% more likely to die of
cardiovascular disease (stroke, heart attack). [Journal Clinical Endocrinology Metabolism June 2015]
Vitamin D and lung disease
Patients
with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and low levels of
vitamin D compared those with the highest vitamin D blood levels have a
340% increased risk of dying from cardiovascular disease. [Clinical Cardiology Aug 2014]
Critically
ill patients with the lowest vitamin D blood levels are 84% more likely
to experience respiratory failure and require a ventilator compared to
patients with the highest vitamin D blood levels. [BMJ Open Respiratory Research June 2015]
Among
critically ill patients who must rely upon a mechanical ventilator to
breathe the mortality rate was 95% among patients with low vitamin D
levels and 40% with high vitamin D levels. [Indian Journal Endocrinology Metabolism July 2014]
Vitamin C and survival
In a study
conducted on a geriatric care ward, patients with scurvy (deficiency of
vitamin C) were far more likely to experience coronary heart disease
(39% vs 9%), need assistance for feeding (56% vs 13% and were more than 7
times more likely to die in the hospital (44% vs 9%). [Journal Nutrition Health Aging June 2010]
The
administration of intravenous vitamin C to terminal cancer patients
whose cancer has spread to bone reduces pain by 55% and prolongs
survival by 10 months, as long as many highly touted anti-cancer drugs. [Alternative Therapies Health Medicine Oct 2014]
Cancer
patients and their families may have a difficult time convincing their
doctors to administer intravenous vitamin C but this is what a recent
review said:
“Intravenous vitamin C (IVC) dosing ranged from 1 gram (1000 milligrams) to more than 200 grams ascorbic acid per infusion, typically administered 2 to 3 times weekly. IVC does not appear to increase toxicity or interfere with antitumor therapy… IVC may improve time to relapse and possibly enhance reductions in tumor mass and improve survival in combination with chemotherapy. IVC may improve quality of life, physical function, and toxicities associated with chemotherapy, including fatigue, nausea, insomnia, constipation, and depression. Case reports document several instances of tumor regression and long-term disease-free survival associated with use of IVC.” [Integrative Cancer Therapy May 2014]
Just 100 milligrams of vitamin C per day reduces the risk of death after a diagnosis of breast cancer by 27%. [European Journal Cancer May 2014]
Three
cases of unexpected long-term survival from severe cases of cancer have
been documented after receiving intravenous vitamin C therapy. [Canadian Medical Assn. Journal March 28, 2006] (See photos below)
Image credits: Canadian Medical Association Inc.
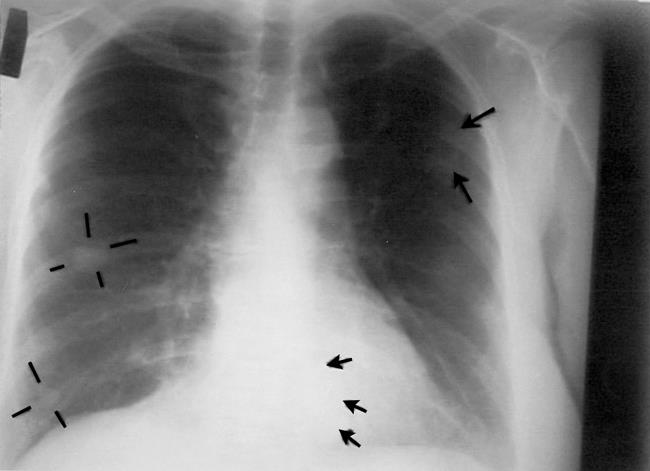
Chest radiography, November 1996, about 1
month after intravenous vitamin C therapy was started. Cannonball
lesions are evident in both lungs, as indicated by the arrows and lines.
Chest radiography, June 1997, showing shrinkage of tumor masses; the arrow indicates one residual abnormality.
Vitamin B1 and acidosis
Critically
ill hospitalized patients are at greater risk of dying from acidosis
(blood is too acid). The standard therapy is to administer pH-balancing
intravenous sodium bicarbonate, an alkaline infusion. However, the
cause of the problem is nutritional. The provision of vitamin B1
(thiamin) reverses acidosis and the risk of death and the need for the
intravenous therapy. [Nutrition Clinical Practice Feb 2015]
Fish oil and cancer
Response
to chemotherapy among patients with non-small cell lung cancer is less
than 30%. Supplementation with fish oil increases the effectiveness of
chemotherapy. Patients taking 2500 milligrams of fish oil/day
experienced greater 1-year survival (60.0%) than patients receiving
standard therapy (38.7%). No toxicity or adverse effects were reported.
[Cancer Aug 2011]
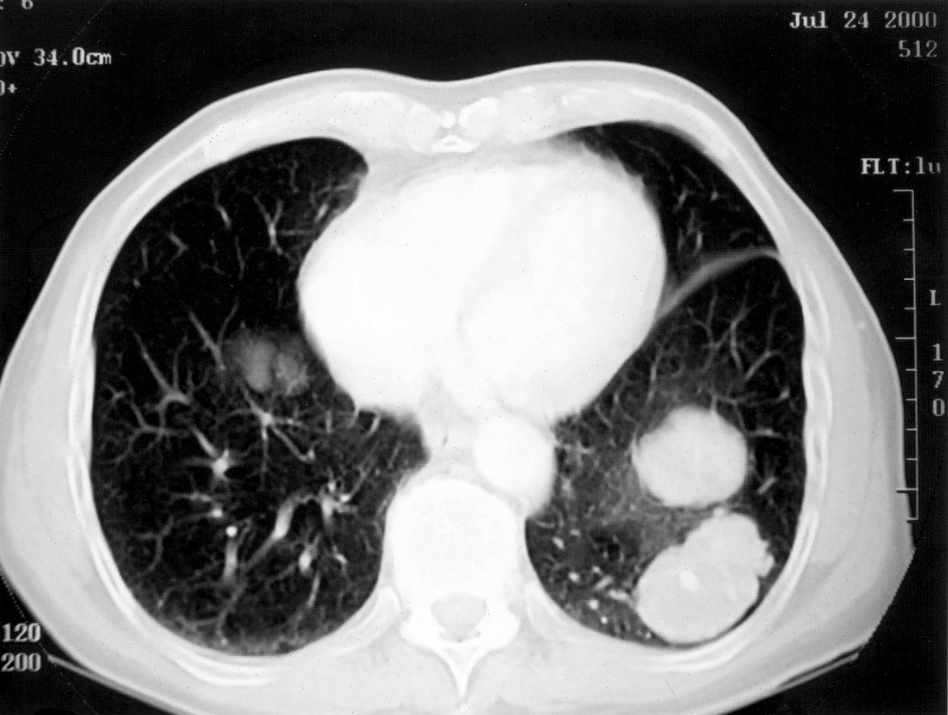
A
78-year old man with an advanced form of lung cancer (malignant fibrous
histiocytoma) declined conventional cancer therapy and elected to
adhere a daily regimen of 15 grams of omega-3 fish oils (8160 mg EPA,
6840 mg DHA) and over a 4-year period experienced a remarkably slow and
steady decrease in the size and number of lung tumors. (see
accompanying photos). [Nutrition & Cancer 2005]
Photo credits: Taylor & Francis, Nutrition & Cancer, Volume 52, 2005
(CT) scan performed on July 24, 2000 reveals two large masses in the lower left lobes of the lung.
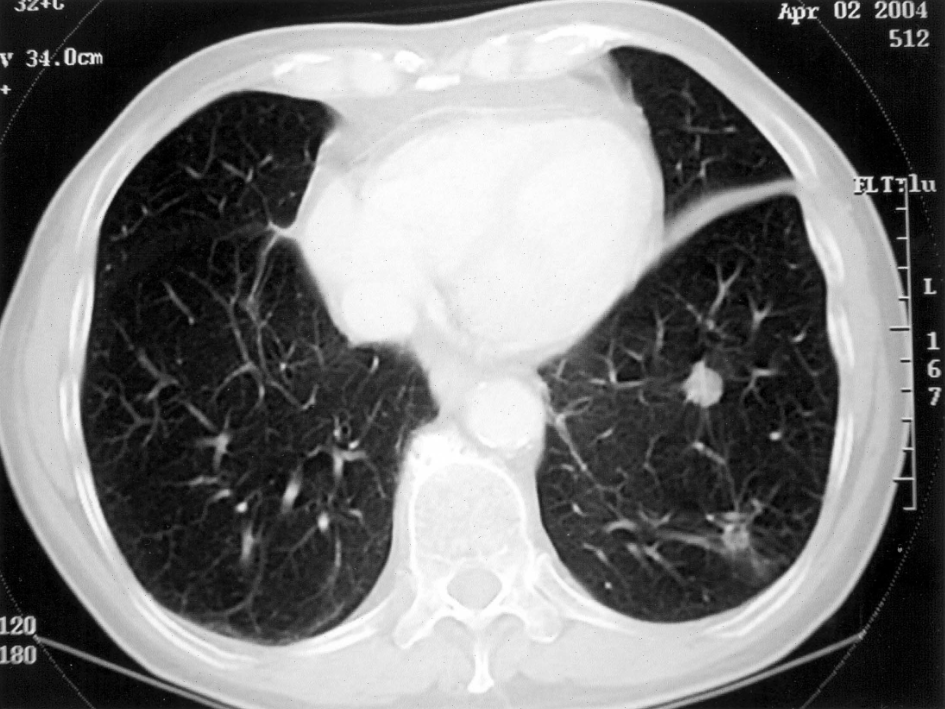
CT scan performed on April 2, 2004. Tumor masses in lower left lobe are greatly diminished in size.
A noted author and researcher emails me to say:
Brother in intensive care update:I had problems with the hospital using any excuse to lower the vitamin C dose or stopping it completely…It went 50-grams for a day, zero for a couple of days, 6 grams for a couple of days then 10-grams.He was making steady recovery on 10-grams a day – starting to sit up etc. Then they stopped the vitamin C completely because of loose stools without telling me. He died 2-days later before we could get the vitamin C reinstated. The stupidity was tragic – literally!
End-of-life consultations
Will
your physician be recommending vitamin C, vitamin D, fish oil or
vitamin B1 to your loved ones with hopeless terminal diseases? I
sincerely doubt they will. Doctors say nutritional therapy is
unproven, but it is certainly not disproven.
Even if these nutritional therapies are of marginal benefit, they are non-toxic and inexpensive. Even if just palliative (relieving pain or alleviating other discomfort) they would serve Medicare patients better than expensive toxic therapies.
Why
is conventional medicine so reticent to conduct more convincing larger
studies that employ nutritional therapy especially among terminal
patients who have little or no hope?
You
can see from the evidence presented here, by not putting nutritional
science into practice they are already culling the population and
reducing Medicare costs by neglectful attrition.

No comments:
Post a Comment