Japan Leads the Way in Child Health: No Compulsory Vaccines. Banned Measles Mumps Rubella (MMR) Vaccine
The Promise of Good Health; Are We Jumping Off the Cliff in the U.S.?
In the United States, many legislators and public health officials are busy trying to make vaccines de facto compulsory—either by removing parental/personal choice given by existing vaccine
exemptions or by imposing undue quarantines and fines on those who do not comply with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC’s) vaccine edicts. Officials in California are seeking to override medical opinion about fitness for vaccination, while those in New York are mandating the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine for 6-12-month-old infants for whom its safety and effectiveness “have not been established.”
The U.S. has the very highest infant mortality
rate of all industrialized developed countries, with more American
children dying at birth and in their first year than in any other
comparable nation—and more than half of those who survive develop at
least one chronic illness.
American children would be better served if these officials—before
imposing questionable and draconian measures—studied child health
outcomes in Japan. With a population of 127 million, Japan has the
healthiest children and the very highest “healthy life expectancy” in the world—and
the least vaccinated children of any developed country. The U.S., in
contrast, has the developed world’s most aggressive vaccination schedule
in number and timing, starting at pregnancy, at birth and in the first
two years of life. Does this make U.S. children healthier? The clear
answer is no. The U.S. has the very highest infant mortality rate of all
industrialized countries, with more American children dying at birth and in their first year than in any other comparable nation—and more than half
of those who survive develop at least one chronic illness. Analysis of
real-world infant mortality and health results shows that U.S. vaccine
policy does not add up to a win for American children.Japan and the U.S.; Two Different Vaccine Policies
In 1994, Japan transitioned away from mandated vaccination in public health centers to voluntary vaccination in doctors’ offices, guided by “the concept that it is better that vaccinations are performed by children’s family doctors who are familiar with their health conditions.” The country created two categories of non-compulsory vaccines: “routine” vaccines that the government covers and “strongly recommends” but does not mandate, and additional “voluntary” vaccines, generally paid for out-of-pocket. Unlike in the U.S., Japan has no vaccine requirements for children entering preschool or elementary school.
Japan also banned the MMR vaccine in the same time frame, due to thousands of serious injuries over a four-year period—producing an injury rate of one in 900 children that was “over 2,000 times higher than the expected rate.” It initially offered separate measles and rubella vaccines following its abandonment of the MMR vaccine; Japan now recommends a combined measles-rubella (MR) vaccine for routine use but still shuns the MMR. The mumps vaccine is in the “voluntary” category.
Here are key differences between the Japanese and U.S. vaccine programs:
- Japan has no vaccine mandates, instead recommending vaccines that (as discussed above) are either “routine” (covered by insurance) or “voluntary” (self-pay).
- Japan does not vaccinate newborns with the hepatitis B (HepB) vaccine, unless the mother is hepatitis B positive.
- Japan does not vaccinate pregnant mothers with the tetanus-diphtheria-acellular pertussis (Tdap) vaccine.
- Japan does not give flu shots to pregnant mothers or to six-month-old infants.
- Japan does not give the MMR vaccine, instead recommending an MR vaccine.
- Japan does not require the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine.
No other developed country administers as many vaccine doses in the first two years of life.
The HepB vaccine injects a newborn with a 250-microgram load of aluminum, a neurotoxic and immune-toxic adjuvant used to provoke an immune response. There are no studies to back up the safety of exposing infants to such high levels of the injected metal. In fact, the Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA’s) upper limit for aluminum in intravenous (IV) fluids for newborns is far lower at five micrograms per kilogram per day (mcg/kg/day)—and even at these levels, researchers have documented the potential for impaired neurologic development. For an average newborn weighing 7.5 pounds, the HepB vaccine has over 15 times more aluminum than the FDA’s upper limit for IV solutions.
Unlike Japan, the U.S. administers flu and Tdap vaccines to pregnant women (during any trimester) and babies receive flu shots at six months of age, continuing every single year thereafter. Manufacturers have never tested the safety of flu shots administered during pregnancy, and the FDA has never formally licensed any vaccines “specifically for use during pregnancy to protect the infant.”
Japan initially recommended the HPV vaccine but stopped doing so in 2013 after serious health problems prompted numerous lawsuits. Japanese researchers have since confirmed a temporal relationship between HPV vaccination and recipients’ development of symptoms.
Japan initially recommended the HPV vaccine but stopped doing so in 2013 after serious health problems prompted numerous lawsuits. Japanese researchers have since confirmed a temporal relationship between HPV vaccination and recipients’ development of symptoms. U.S. regulators have ignored these and similar reports and not only continue to aggressively promote and even mandate the formerly optional HPV vaccine beginning in preadolescence but are now pushing it in adulthood. The Merck-manufactured HPV vaccine received fast-tracked approval from the FDA despite half of all clinical trial subjects reporting serious medical conditions within seven months.
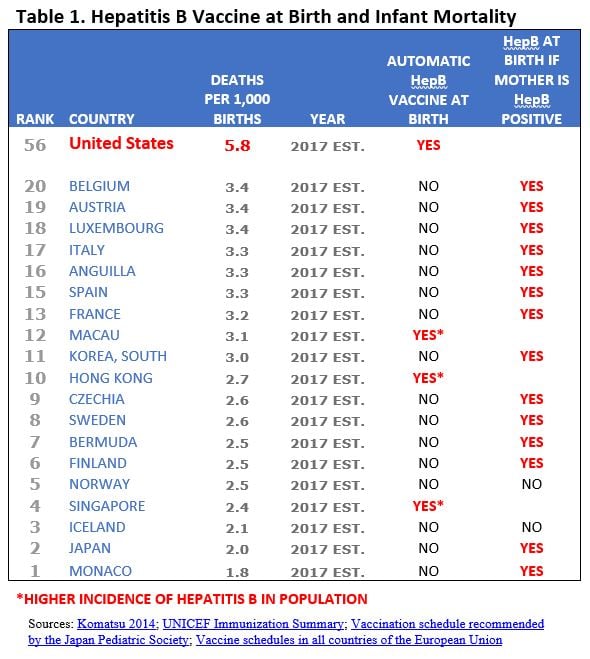
Best and Worst: Two Different Infant Mortality Results
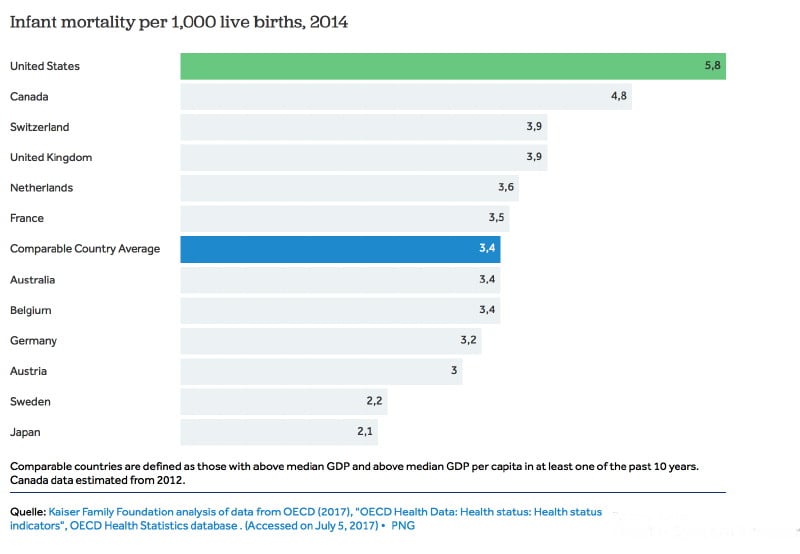
The CDC views infant mortality as one of the most important indicators of a society’s overall health. The agency should take note of Japan’s rate, which, at 2 infant deaths per 1,000 live births, is the second lowest in the world, second only to the Principality of Monaco. In comparison, almost three times as many American infants die (5.8 per 1,000 live births), despite massive per capita spending on health care for children (see Table 2). U.S. infant mortality ranks behind 55 other countries and is worse than the rate in Latvia, Slovakia or Cuba.
If vaccines save lives, why are American children
dying at a faster rate, and…dying younger compared to children in 19
other wealthy countries—translating into a 57 percent greater risk of
death before reaching adulthood?
To reiterate, the U.S. has the most aggressive vaccine schedule of
developed countries (administering the most vaccines the earliest). If
vaccines save lives, why are American children “dying at a faster rate,
and…dying younger” compared to children in 19 other wealthy countries—translating into a “57 percent greater risk of death
before reaching adulthood”? Japanese children, who receive the fewest
vaccines—with no government mandates for vaccination—grow up to enjoy “long and vigorous” lives. International
infant mortality and health statistics and their correlation to
vaccination protocols show results that government and health officials
are ignoring at our children’s great peril.Among the 20 countries with the world’s best infant mortality outcomes, only three countries (Hong Kong, Macau and Singapore) automatically administer the HepB vaccine to all newborns—governed by the rationale that hepatitis B infection is highly endemic in these countries. Most of the other 17 top-ranking countries—including Japan—give the HepB vaccine at birth only if the mother is hepatitis B positive (Table 1). The U.S., with its disgraceful #56 infant mortality ranking, gives the HepB vaccine to all four million babies born annually despite a low incidence of hepatitis B.
Is the U.S. Sacrificing Children’s Health for Profits?
Merck, the MMR vaccine’s manufacturer, is in court over MMR-related fraud. Whistleblowers allege the pharmaceutical giant rigged its efficacy data for the vaccine’s mumps component to ensure its continued market monopoly. The whistleblower evidence has given rise to two separate court cases. In addition, a CDC whistleblower has alleged the MMR vaccine increases autism risks in some children. Others have reported that the potential risk of permanent injury from the MMR vaccine dwarfs the risks of getting measles.
Why do the FDA and CDC continue to endorse the problematic MMR vaccine despite Merck’s implication in fraud over the vaccine’s safety and efficacy? Why do U.S. legislators and government officials not demand a better alternative, as Japan did over two decades ago? Why are U.S. cities and states forcing Merck’s MMR vaccine on American children? Is the U.S. government protecting children, or Merck? Why are U.S. officials ignoring Japan’s exemplary model, which proves that the most measured vaccination program in the industrialized world and “first-class sanitation and levels of nutrition” can produce optimal child health outcomes that are leading the world?
A central tenet of a free and democratic society is the freedom to make informed decisions about medical interventions that carry serious potential risks. This includes the right to be apprised of benefits and risks—and the ability to say no. The Nuremberg Code of ethics established the necessity of informed consent without “any element of force, fraud, deceit, duress, over-reaching, or other ulterior form of constraint or coercion.” Forcing the MMR vaccine, or any other vaccine, on those who are uninformed or who do not consent represents nothing less than medical tyranny.
*
Note to readers: please click the share
buttons below. Forward this article to your email lists. Crosspost on
your blog site, internet forums. etc.
Featured image is from Children’s Health Defense
The original source of this article is Children's Health Defense
Copyright © Kristina Kristen, Children's Health Defense, 2019
Comment on Global Research Articles on our Facebook page
Become a Member of Global Research
No comments:
Post a Comment